Liver disease is a global health challenge, affecting millions each year. The liver has a remarkable ability to regenerate; however, chronic damage arising from obesity, alcohol, or metabolic dysfunction can lead to irreversible failure. At the University of Edinburgh’s Centre for Regenerative Medicine, Professor David Hay’s lab is developing innovative ways to study liver function and disease using a lab-grown mini-organ. In this blog, we highlight how Dr. Hay’s lab is redefining liver disease research through 3D models that reveal how hormones influence metabolic health.
Continue reading “Insights from 3D Liver Models: Rethinking Fatty Liver Disease with Hormone Correction”3D cell culture
What Makes OBI-992 Different? A Closer Look at This TROP2 Antibody Drug Conjugate
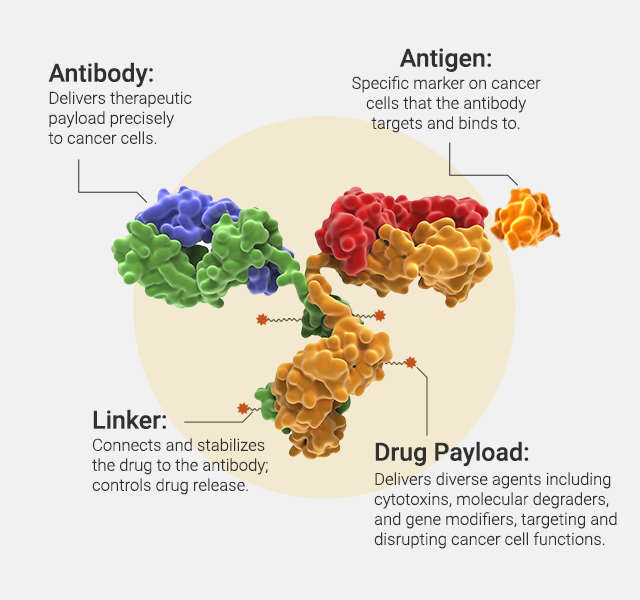
Antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) are an increasingly powerful class of cancer therapeutics that combine the targeted precision of monoclonal antibodies with the cytotoxic potency of small-molecule drugs. By directing chemotherapy agents specifically to tumor cells, ADCs aim to maximize antitumor activity while minimizing damage to healthy tissues. One key challenge in ADC design is selecting the right target and payload—features that define efficacy, safety and resistance.
Continue reading “What Makes OBI-992 Different? A Closer Look at This TROP2 Antibody Drug Conjugate”What 32,000 3D Spheroids Revealed About Culture Conditions

Three-dimensional (3D) cell culture systems have become essential tools in cancer research, drug screening and tissue engineering—offering a more physiologically relevant alternative to traditional 2D cultures, which often fail to replicate key in vivo microenvironment features. But as the field has evolved, variability in experimental outcomes has become a key challenge, limiting their reproducibility and translation into clinical settings. While spheroids offer layered architecture, nutrient gradients and multicellular interactions, inconsistent culture methods have made it difficult to draw reliable conclusions across labs.
Continue reading “What 32,000 3D Spheroids Revealed About Culture Conditions”Cellular Senescence and Cancer Therapy: Overcoming Immortality?
At the time of writing this post, no scientist had yet discovered the secret to immortality. In our world, we’ve come to accept that living things are born, grow old and die—the circle of life.
And yet, for many years, life scientists believed that the circle of life did not apply to our constituent cells when cultured in a laboratory. That is, cultured normal human cells were immortal, and they would continue to grow and proliferate forever, as long as they were provided with the necessary nutrients.
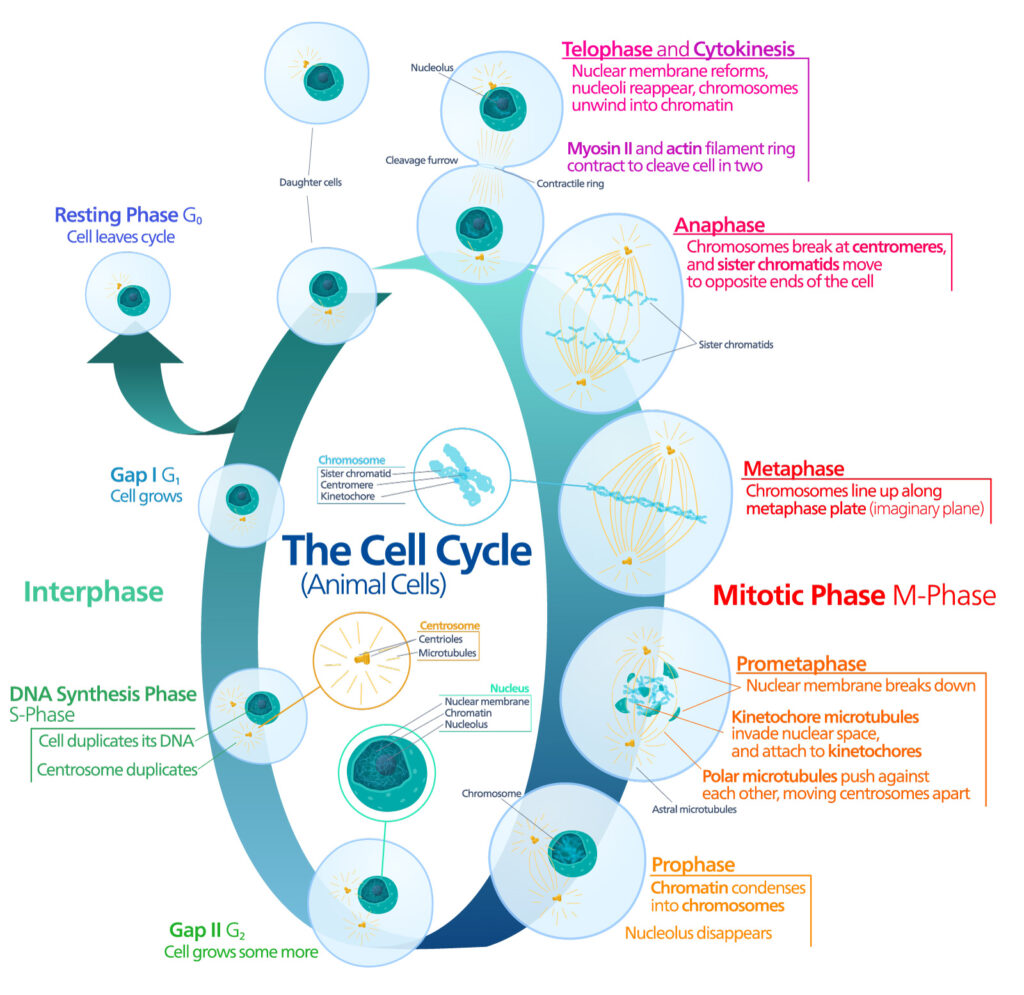
Pioneering work published in 1961 by Leonard Hayflick and Paul Moorhead challenged that theory (reviewed in 1). Their research showed that normal cells in culture have a finite capacity to replicate. After they reach a certain number of replicative cycles, cells stop dividing. Hayflick and Moorhead made the important distinction between normal human cells and cultured cancer cells, which are truly immortal. In later years, the limit to the number of replicative cycles normal human cells can undergo became known as the Hayflick limit. Although some scientists still express skepticism about these findings, the Hayflick limit is widely recognized as a fundamental principle of cell biology.
Continue reading “Cellular Senescence and Cancer Therapy: Overcoming Immortality?”Cytochrome P450 Inhibition: Old Drug, New Tricks

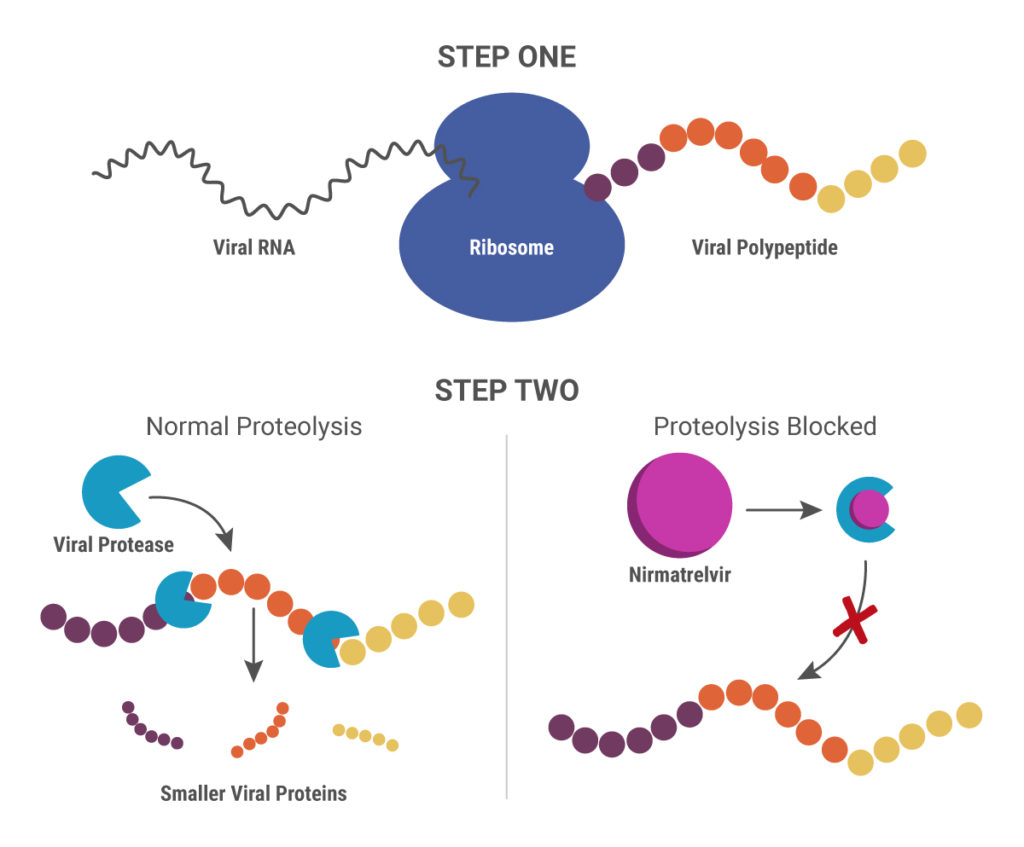
Cytochrome P450 (CYP) inhibitors are often used as boosting agents in combination with other drugs. This drug development strategy is front and center for Paxlovid, the new anti-SARS-CoV-2 treatment from Pfizer. Paxlovid is a combination therapy, comprised of two protease inhibitors, nirmatrelvir and ritonavir. It significantly reduces the risk of COVID-19 hospitalization in high-risk adults and is ingested orally rather than injected, which is an advantage over other SARS-CoV-2 treatments, such as Remdesivir.
Nirmatrelvir was originally developed by Pfizer almost 20 years ago to treat HIV and works by blocking enzymes that help viruses replicate. Pfizer created another version of this drug to combat SARS in 2003, but, once that outbreak ended, further development was put on pause until the advent of the COVID-19 pandemic. After developing an intravenous form of nirmatrelvir early in the pandemic, Pfizer created another version that can be taken orally and combined it with ritonavir.
When ritonavir was originally developed, it wasn’t considered particularly useful because it metabolized so quickly in the body. Now it is recognized as a pharmacokinetic enhancer in combination with other drugs. Ritonivir inhibits CYP3A4, an enzyme which plays a key role in the metabolism of drugs and xenobiotics. By inhibiting CYP3A4, ritonivir slows the metabolism of other drugs. In the case of Paxlovid, this allows nirmatrelvir to stay in the body longer at a high enough concentration to be effective against the virus. This ultimately means that patients can be given lower doses of the drug with reducing efficacy.
3D Cell Culture Models: Challenges for Cell-Based Assays
In 3D cell culture models, cells are grown under conditions that allow the formation of multicellular spheroids or microtissues. Instead of growing in a monolayer on a plate surface, cells in 3D culture grow within a support matrix that allows them to interact with each other, forming cell:cell connections and creating an environment that mimics the situation in the body more closely than traditional 2D systems. Although 3D cultures are designed to offer a more physiologically accurate environment, the added complexity of that environment can also present challenges to experimental design when performing cell-based assays. For example, it can be a challenge for assay reagents to penetrate to the center of larger microtissues and for lytic assays to disrupt all cells within the 3D system.
Earlier this week Terry Riss, a Senior Product Specialist at Promega, presented a Webinar on the challenges of performing cell-based assays on microtissues in 3D cell culture. During the Webinar, Terry gave an overview of the different methods available for 3D cell culture, providing a description of the advantages of each. He then discussed considerations for designing and optimizing cell-based assays for use in 3D culture systems, providing several recommendations to keep in mind when performing cell viability assays on larger microtissue samples.
Continue reading “3D Cell Culture Models: Challenges for Cell-Based Assays”Overcoming Challenges to Detect Apoptosis in 3D Cell Structures
This blog is written by guest author, Maggie Bach, Sr. Product Manager, Promega Corporation.
Researchers are increasingly relying on cells grown in three-dimensional (3D) structures to help answer their research questions. Monolayer, or 2D cell culture, was the go-to cell culture method for the past century. Now, the need to better represent in vivo conditions is driving the adoption of 3D cell culture models. Cells grown in 3D structures better mimic tissue-like structures, better exhibit differentiated cellular functions, and better predict in vivo responses to drug treatment.
Switching to 3D cell culture models comes with challenges. Methods to interrogate these models need to be adaptable and reliable for the many types of 3D models. Some of the most popular 3D models include spheroids grown in ultra-low attachment plates, and cells grown in an extracellular matrix, such as Matrigel® from Corning. Even more complex models include medium flow over the cells in microfluidic or organ-on-a-chip devices. Will an assay originally developed for cells grown in monolayer perform consistently with various 3D models? How is measuring a cellular marker different when cells are grown in 3D models compared to monolayer growth?

Producing Snake Venom— in the Lab

Snakebite is a serious public health issue in many tropical countries. Every year, roughly 2 million cases of poisoning from snakebites occur, and more than 100,000 people die. Snake venom is extremely complex, containing a cocktail of chemicals, many of which are undefined. This complicates the development of new therapeutics for treating snakebite.
Antivenom is the most effective treatment for snakebites, but its production is complex and dangerous. It involves manually milking the venom from different species of live snakes, then injecting small doses of the venom into animals (mostly horses) to stimulate an immune response. After a period of time, antibodies form in the animal’s blood, which is purified for use as antivenom.
But what if we could produce snake venom in the lab, instead of using live snakes? Recently, a group from the Netherlands did just that by growing organoids derived from snake venom glands.
Continue reading “Producing Snake Venom— in the Lab”Reliable DNA Purification from 3D Cell Cultures
Traditionally, scientists have relied on flat, two-dimensional cell cultures grown on substrates such as tissue culture polystyrene (TCPS) to study cellular physiology. These models are simple and cost-effective to culture and process. Within the last decade, however, three-dimensional (3D) cell cultures have become increasingly popular because they are more physiologically relevant and better represent in vivo conditions.
Improving Cancer Drug Screening with 3D Cell Culture