The global war against the coronavirus that causes COVID-19 rages on, spearheaded by efforts to develop effective and safe vaccines. At the time of writing, over 100 COVID-19 vaccine clinical trials were listed in the clinicaltrials.gov database. Recent attention has focused on mRNA vaccines developed by Pfizer/BioNTech and Moderna. If licensed, they would become the first mRNA vaccines for human use.
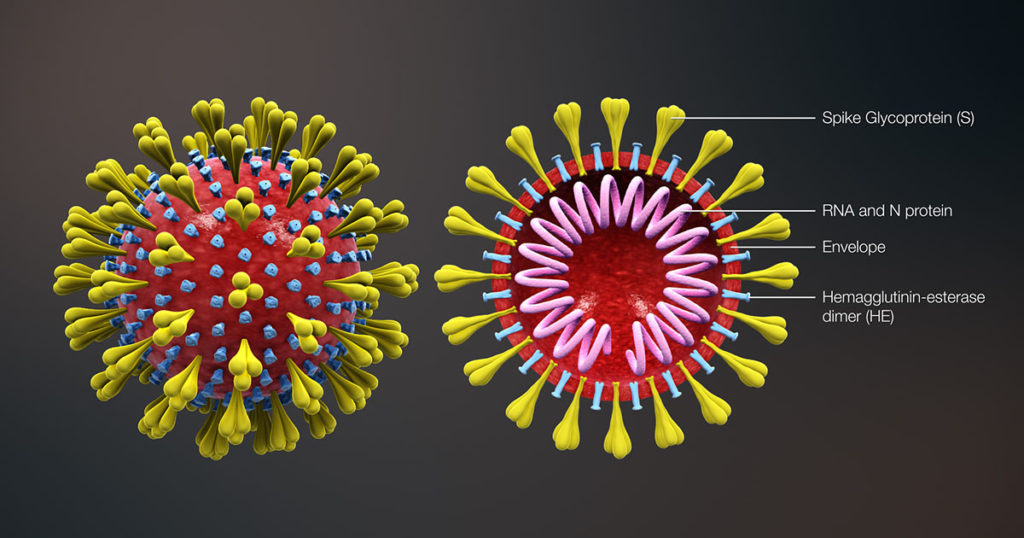
Other vaccine development efforts are relying on more conventional techniques—using an adenoviral vector to deliver a DNA molecule that encodes the SARS-CoV-2 spike (S) protein. Examples of these adenoviral vector vaccines include the vaccines from Oxford University/AstraZeneca (the UK), Cansino Biologics (China), Sputnik V (Russia) and Janssen Pharmaceuticals/Johnson & Johnson (the Netherlands and USA).