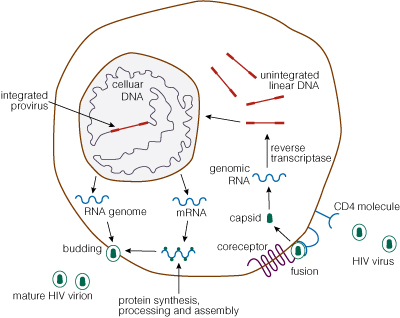
Today’s blog is written by guest blogger, Sameer Moorji, Director, Applied Markets.
People’s diets are frequently influenced by a wide range of variables; with environment, socioeconomic status, religion, and culture being a few of the key influencers. The Muslim community serves as one illustration of how culture and religion can hold influence over people’s eating habits.

Muslims, who adhere to Islamic teachings derived from the Qur’an, frequently base dietary choices on a food’s halal status, whether it is permissible to consume, or haram status, forbidden to consume. With the population of Muslims expected to expand from 1.6 billion in 2010 to 2.2 billion by 2030, the demand for halal products is anticipated to surge (2).
By 2030, the global halal meat market is projected to reach over $300 billion dollars, with Asia-Pacific and the Middle East regions being the largest consumers and producers of halal meat products (3). Furthermore, increasing awareness and popularity of halal meat among non-Muslim consumers, as well as strengthening preference for ethical and high-quality meat, are all contributing to demand.
Continue reading “No Horsin’ around with Halal Meat Authentication”