Cytochrome P450 (CYP) inhibitors are often used as boosting agents in combination with other drugs. This drug development strategy is front and center for Paxlovid, the new anti-SARS-CoV-2 treatment from Pfizer. Paxlovid is a combination therapy, comprised of two protease inhibitors, nirmatrelvir and ritonavir. It significantly reduces the risk of COVID-19 hospitalization in high-risk adults and is ingested orally rather than injected, which is an advantage over other SARS-CoV-2 treatments, such as Remdesivir.
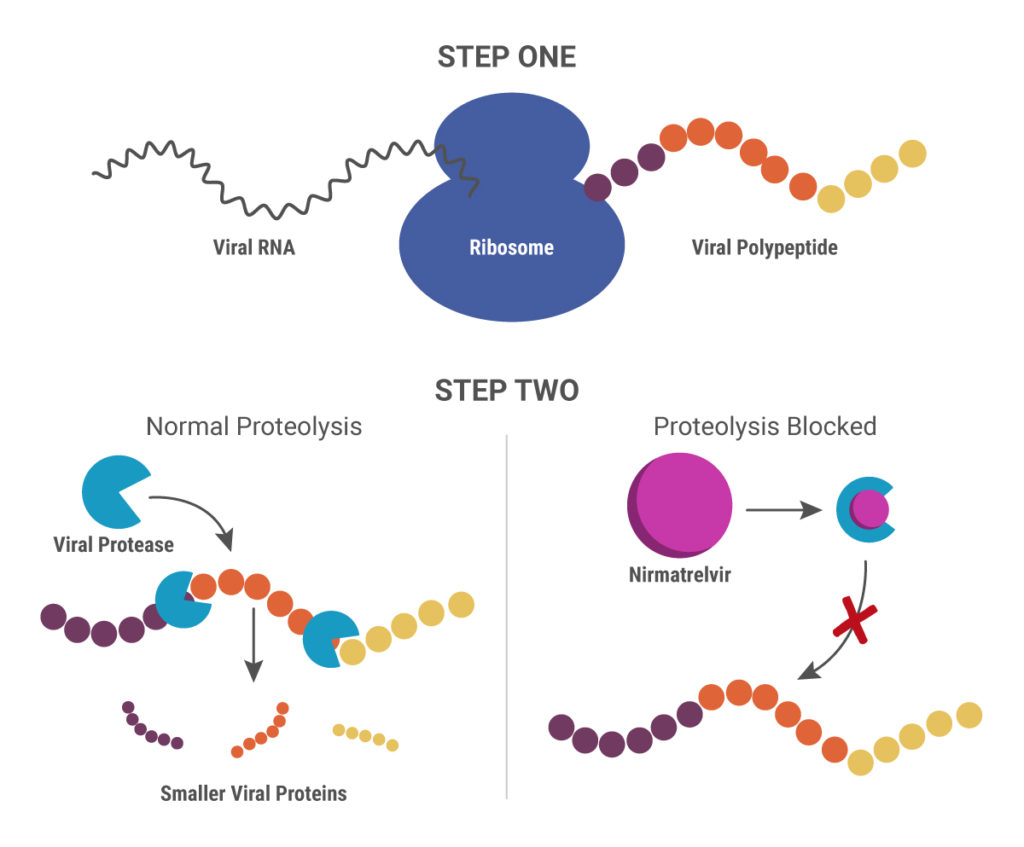
Nirmatrelvir was originally developed by Pfizer almost 20 years ago to treat HIV and works by blocking enzymes that help viruses replicate. Pfizer created another version of this drug to combat SARS in 2003, but, once that outbreak ended, further development was put on pause until the advent of the COVID-19 pandemic. After developing an intravenous form of nirmatrelvir early in the pandemic, Pfizer created another version that can be taken orally and combined it with ritonavir.
When ritonavir was originally developed, it wasn’t considered particularly useful because it metabolized so quickly in the body. Now it is recognized as a pharmacokinetic enhancer in combination with other drugs. Ritonivir inhibits CYP3A4, an enzyme which plays a key role in the metabolism of drugs and xenobiotics. By inhibiting CYP3A4, ritonivir slows the metabolism of other drugs. In the case of Paxlovid, this allows nirmatrelvir to stay in the body longer at a high enough concentration to be effective against the virus. This ultimately means that patients can be given lower doses of the drug with reducing efficacy.