CRISPR is a hot topic right now, and rightly so—it is revolutionizing research that relies on editing genes. But what exactly is CRISPR? How does it work? Why is everyone so interested in using it? Today’s blog is a beginner’s guide on how CRISPR works with an overview of some new applications of this technology for those familiar with CRISPR.
Introduction to CRISPR/Cas9
Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats (CRISPR) were discovered in 1987, but it took 30 years before scientists identified their function. CRISPRs are a special kind of repeating DNA sequence that bacteria have as part of their “immune” system against invading nucleic acids from viruses and other bacteria. Over time, the genetic material from these invaders can be incorporated into the bacterial genome as a CRISPR and used to target specific sequences found in foreign genomes.
CRISPRs are part of a system within a bacterium that requires a nuclease (e.g. Cas9), a single guide RNA (sgRNA) and a tracrRNA. The tracrRNA recruits Cas9, while sgRNA binds to Cas9 and guides it to the corresponding DNA sequence of the invading genome. Cas9 then cuts the DNA, creating a double-stranded break that disables its function. Bacteria use a Protospacer Adjacent Motif, or PAM, sequence near the target sequence to distinguish between self and non-self and protect their own DNA.
While this system is an effective method of protection for bacteria, CRISPR/Cas9 has been manipulated in order to perform gene editing in a lab (click here for a video about CRISPR). First, the tracrRNA and sgRNA are combined into a single molecule. Then the sequence of the guide portion of this RNA is changed to match the target sequence. Using this engineered sgRNA along with Cas9 will result in a double-stranded break (DSB) in the target DNA sequence, provided the target sequence is adjacent to a compatible PAM sequence.
Continue reading “A Crash Course in CRISPR” Like this:
Like Loading...



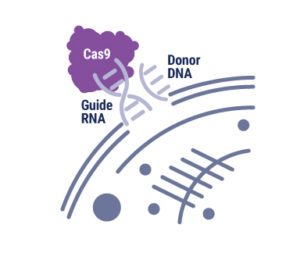
 There are new developments in genetics coming to light every day, each with the potential to dramatically change life as we know it. The increasingly controversial gene editing system, dubbed CRISPR (Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats), is at the root of it all. Harnessed for use in genome editing in 20131, CRISPR has given hope to researchers looking to solve various biological problems. It’s with this technology that researchers anticipate eventually having the means to genetically modify humans and rid society of genetic disorders, such as hemophilia. While this is not yet possible, the building blocks are steadily being developed. Most recently, two groundbreaking studies concerning CRISPR have been released to the public.
There are new developments in genetics coming to light every day, each with the potential to dramatically change life as we know it. The increasingly controversial gene editing system, dubbed CRISPR (Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats), is at the root of it all. Harnessed for use in genome editing in 20131, CRISPR has given hope to researchers looking to solve various biological problems. It’s with this technology that researchers anticipate eventually having the means to genetically modify humans and rid society of genetic disorders, such as hemophilia. While this is not yet possible, the building blocks are steadily being developed. Most recently, two groundbreaking studies concerning CRISPR have been released to the public. 