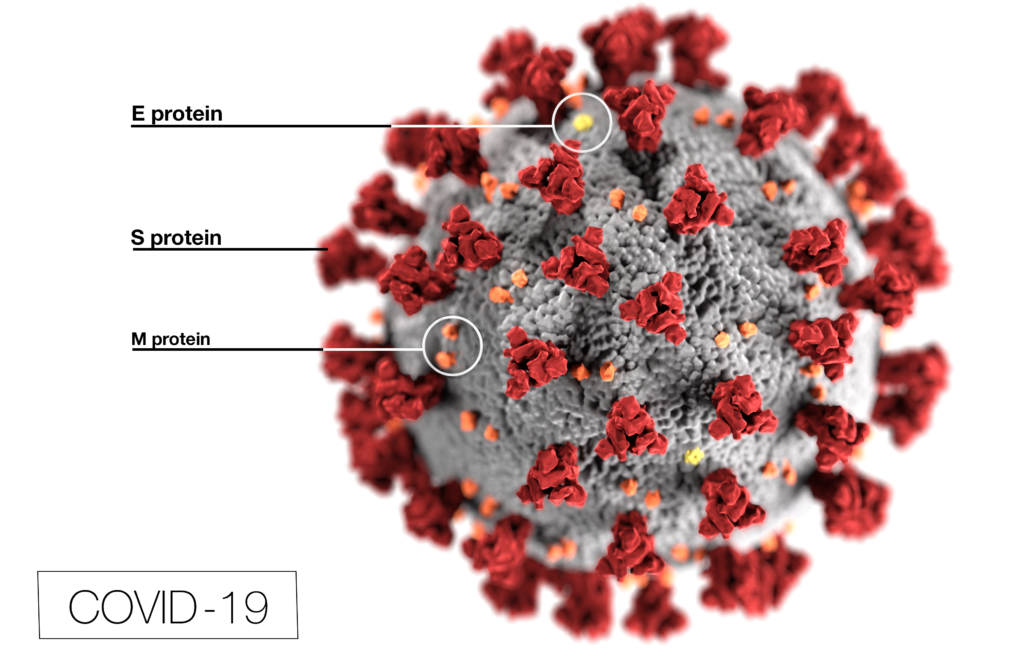
Coronavirus (CoV) researchers are working quickly to understand the entry of SARS-CoV-2 into cells. The Spike or S proteins on the surface of a CoV is trimer. The monomer is composed of an S1 and S2 domain. The division of S1 and S2 happens in the virus producing cell through a furin cleavage site between the two domains. The trimer binds to cell surface proteins. In the case of the SARS-CoV, the receptor is angiotensin converting enzyme 2. (ACE2). The MERS-CoV utilizes the cell-surface dipeptidyl peptidase IV protein. SARS-CoV-2 uses ACE2 as well. Internalized S protein goes though a second cleavage by a host cell protease, near the S1/S2 cleavage site called S2′, which leads to a drastic change in conformation thought to facilitate membrane fusion and entry of the virus into the cell (1).
Rather than work directly with the virus, researchers have chosen to make pseudotyped viral particles. Pseudotyped viral particles contain the envelope proteins of a well-known parent virus (e.g., vesicular stomatitis virus) with the native host cell binding protein (e.g., glycoprotein G) exchanged for the host cell binding protein (S protein) of the virus under investigation. The pseudotyped viral particle typically carries a reporter plasmid, most commonly firefly luciferase (FLuc), with the necessary genetic elements to be packaged in the particle.
To create the pseudotyped viral particle, plasmids or RNA alone are transfected into cells and the pseudotyped viruses work their way through the endoplasmic reticulum and golgi to bud from the cells into the culture medium. The pseudoviruses are used to study the process of viral entry via the exchanged protein from the virus of interest. Entry is monitored through assay of the reporter. The reporter could be a luciferase or a fluorescent protein.
Continue reading “Choices for Measuring Luciferase-Tagged Reporter Pseudotyped Viral Particles in Coronavirus Research”