Cannabinoids. What are they? Sometimes, Wikipedia can give a nice definition:
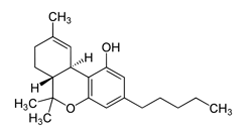
Synthetic cannabinoids (SCs) were originally created for the scientific investigation of two cannabinoid receptors, CB1 and CB2, but have made their way to the streets as “safe” and “legal” alternatives to marijuana.
The problem is that these SCs engage the cannabinoid receptors more completely and with higher affinity than anything derived from marijuana. As a result, SCs can produce serious side effects that often require medical attention. In fact, you are 30 times more likely to seek emergency medical attention following the use of an SC than with natural cannabinoid sources like marijuana.
Continue reading “Bioassay for Cannabinoid Receptor Agonists Designed with NanoBiT™ Techology”