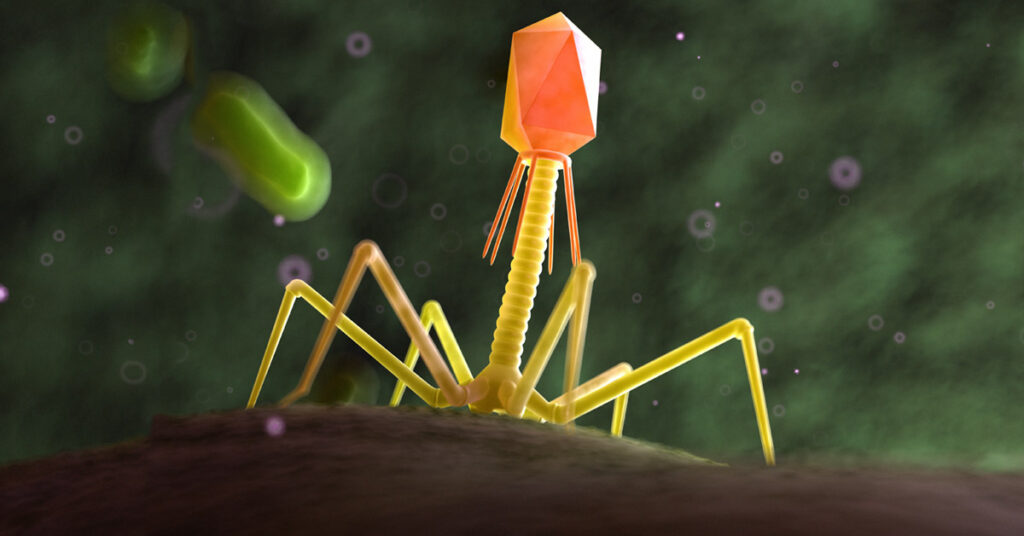
Monitoring and quantifying drug-target binding in a live-cell setting is important to bridging the gap between in vitro assay results and the phenotypic outcome, and therefore represents a crucial step in target validation and drug development (1). The NanoBRET™ Target Engagement (TE) assay is a biophysical technique that enables quantitative assessment of small molecule-target protein binding in live cells. This live-cell target engagement assay uses the bioluminescence resonance energy transfer (BRET) from a NanoLuc® luciferase-tagged target protein and a cell-permeable fluorescent tracer that reversibly binds the target protein of interest. In the presence of unlabeled test compound that engages the target protein, the tracer is displaced, and a loss of BRET signal is observed. Due to the tight distance constraints for BRET, the signal measured is specific to the target fused to NanoLuc® luciferase.
Promega offers over 400 ready-to-use assays for multiple target classes, including kinases, E3 ligases, RAS, and many others. For targets that do not have an existing NanoBRET™ TE assay, Promega offers NanoBRET™ dyes, NanoLuc® cloning vectors, and NanoBRET™ detection reagents to develop novel NanoBRET™ TE assays.
To learn more about the NanoBRET™ TE platform, see the NanoBRET™ Target Engagement Technology Page on our website.
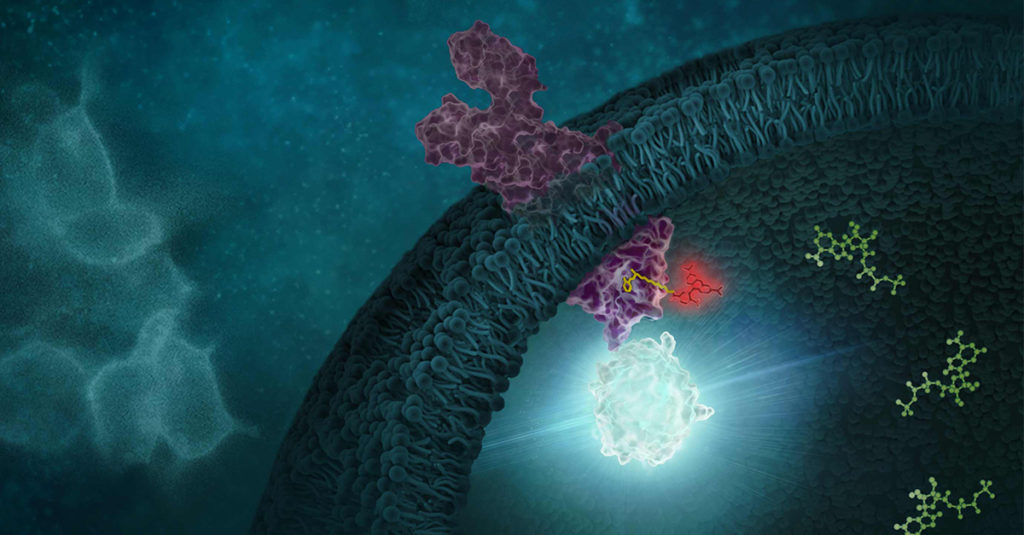
One critical component in the development of novel NanoBRET™ TE assay is the creation of the cell-permeable fluorescent tracers (NanoBRET™ tracers) against the target protein of interest. The tracers are bifunctional, consisting of a NanoBRET™-compatible fluorophore and a target-binding moiety connected by a linker. While the NanoBRET™ 590 dyes have demonstrated consistently robust cell permeability and optimal spectral overlap with NanoLuc® for BRET, a ligand capable of binding to the target protein of interest needs to be identified to generate a NanoBRET™ tracer.
What Are DNA-Encoded Libraries?
DNA-Encoded Libraries, (DELs), have emerged as powerful tools for discovering small molecule ligands to target proteins of interest at an unprecedented scale. . owing to the ability of a DEL to enable the synthesis of larger libraries of compounds and to target proteins without any prior structural knowledge of the proteins or their ligands (2). Because each member of a DEL contains a DNA barcode and a small molecule separated by a linker, DEL is primed for discovering leads within therapeutic modalities that rely on bifunctional chemistry, such as proteolysis targeting chimeras (PROTACs). Since NanoBRET™ tracers are also bifunctional, ligands identified from DEL selections could serve as ideal candidates for developing novel NanoBRET™ tracers that can enable NanoBRET™ TE assays for new targets.
Continue reading “From Hit to Live-Cell Target Engagement Assay: DNA-Encoded Library Screens and NanoBRET™ Dye”