Imagine you’re taking a refreshing night swim in the warm blue waters of Vieques in Puerto Rico. You splash into the surf and head out to some of the deeper waters of the bay, when what to your wondering eyes should appear, but blue streaks of light in water that once was clear. Do you need to get your eyes checked? Are you hallucinating? No! You’ve just happened upon a cluster of dinoflagellates, harmless bioluminescent microorganisms called plankton, that emit their glow when disturbed by movement. These dinoflagellates are known to inhabit waters throughout the world but are generally not present in large enough numbers to be noticed. There are only five ecosystems in the world where these special bioluminescent bays can be seen, and three of them are in Puerto Rico.
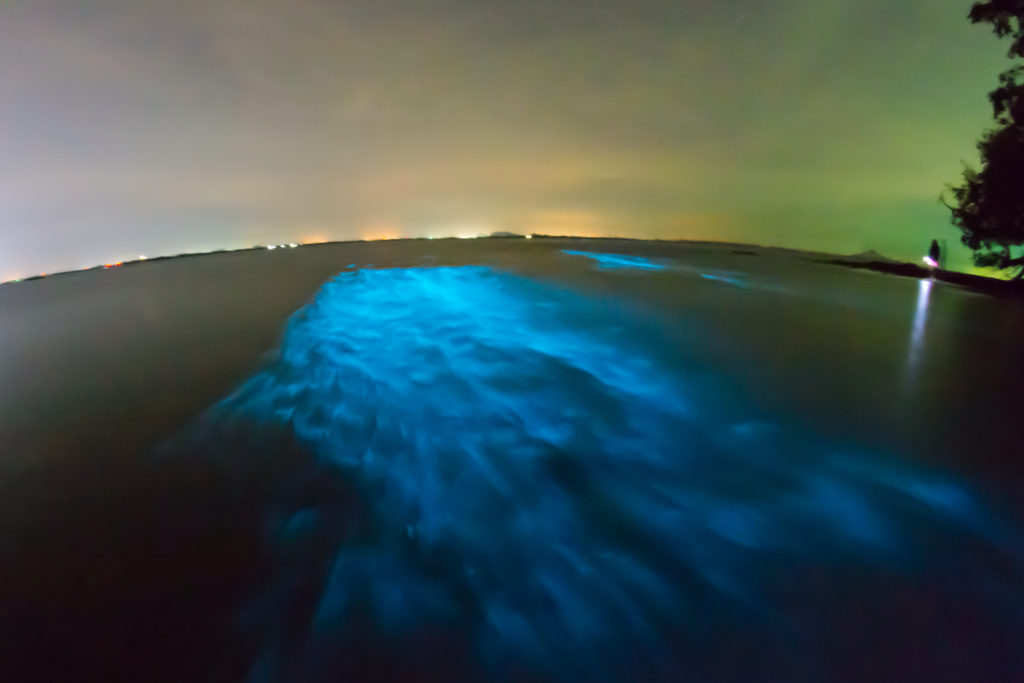

But you don’t have to travel to Puerto Rico or swim with plankton to see bioluminescence. There are bioluminescent organisms all over the world in many unexpected places. There are bioluminescent mushrooms, bioluminescent sea creatures—both large and small (squid, jellyfish, and shrimp, in addition to the dinoflagellates)—and bioluminescent insects, to name a few. Bioluminescence is simply the ability of living things to produce light.
Continue reading “Bioluminescence and Biotechnology: Shining Nature’s Cool Light on Biology”