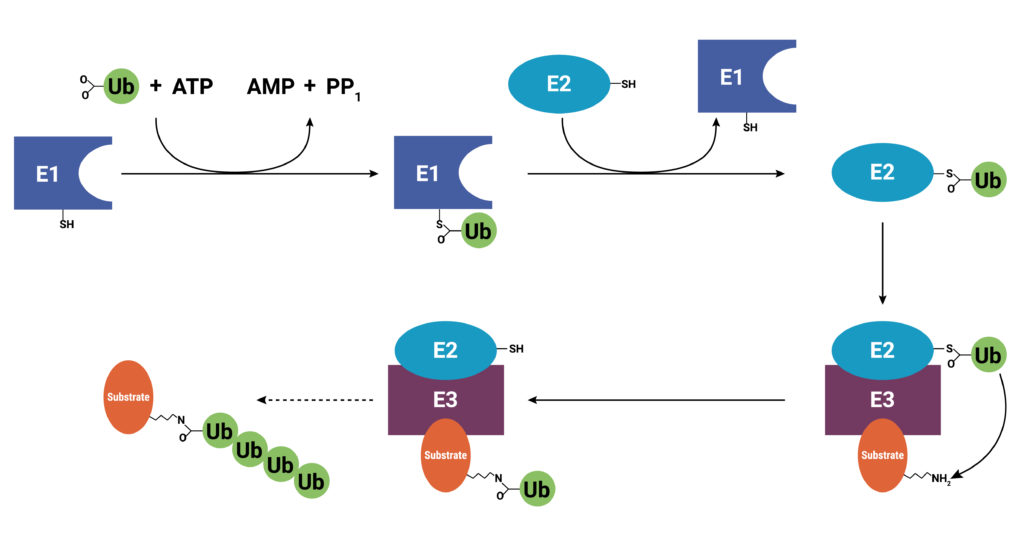
World Art Day embraces art as a means for nurturing creativity and innovation, gaining greater understanding of cultural experiences that are different from our own, and showcasing the contributions of art and artists to sustainable development. It is no accident that World Art Day is celebrated on the birthday of Leonardo da Vinci, the celebrated Italian polymath who used art to express emotions, articulate technological concepts well before their time, and understand the workings of human anatomy.
Takaski Mitachi, a moderator of the 2019 global conference panel on Innovation through Art: Leveraging Disruption for a Sustainable Ecosystem, said that “Art can add value so that we could drive innovation beyond logic and data.” In a sense, the fine arts are a way of expressing our observations about the world around us, similar to how an original scientific hypothesis attempts to explain phenomena we observe and want to test. While scientific investigation builds on data and logic to test a hypothesis, art gives us a different way of knowing our world that extends beyond just data and logic. When we explore the arts, we broaden our understanding and interpretation of the world and bring these new perspectives to our scientific and technological explorations. Art is a disruptor of staid ways of thinking about and approaching problems, and like many other disruptors in our world, it can drive innovation.
In an article in the MIT Technology Review, author Sarah Lewis discusses the relationship between the arts and scientific breakthroughs. She notes one study that found a disproportionately high number of Nobel Prize-winning scientists also pursue art, writing or music as serious avocations. When asked why achievement in art and science seem to go together, she replied: “What the arts allow us to do is develop the muscle required for discernment and also strengthen our sense of agency to determine for ourselves how we’re going to tackle a given problem…Ultimately it’s up to the person creating the work to determine what that path is, and that kind of agency is what’s required for innovation.”
Continue reading “World Art Day: Experiences of Fine Art That Disrupt and Drive Innovation”