Forty-some years ago fat was just fat. And it was regarded with disdain, to say the least.
An entire industry existed to help get rid of fat, using what was then the latest mass media technology, television. If you wanted to get rid of fat you could exercise with Jack LaLanne as he worked out on television. We exercised in elementary school PE class to a vinyl recording of “Chicken Fat”. You could strap into a device that employed shaking to get rid of the fat from your “hips”, or eat a piece of chocolate fudge with a hot beverage before meals to curb your appetite.
Fat was not our friend. We knew long before the current diabetes epidemic that being overweight was not good for our health.
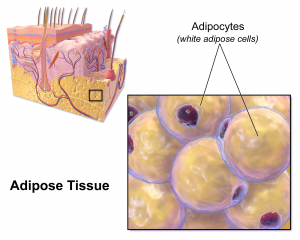
Fast forward to the 21st century, where we’ve learned that some forms of fat are actually good for you–important in metabolism, growth and immunity. The variety of types of mammalian fat include brown adipose tissue, beige adipose tissue and white adipose tissue, and it’s possible to convert one to the other under certain conditions. For details on these types of adipose tissue, read this article —after you finish this blog.
Continue reading “A Surprising New Role for Body Fat?”