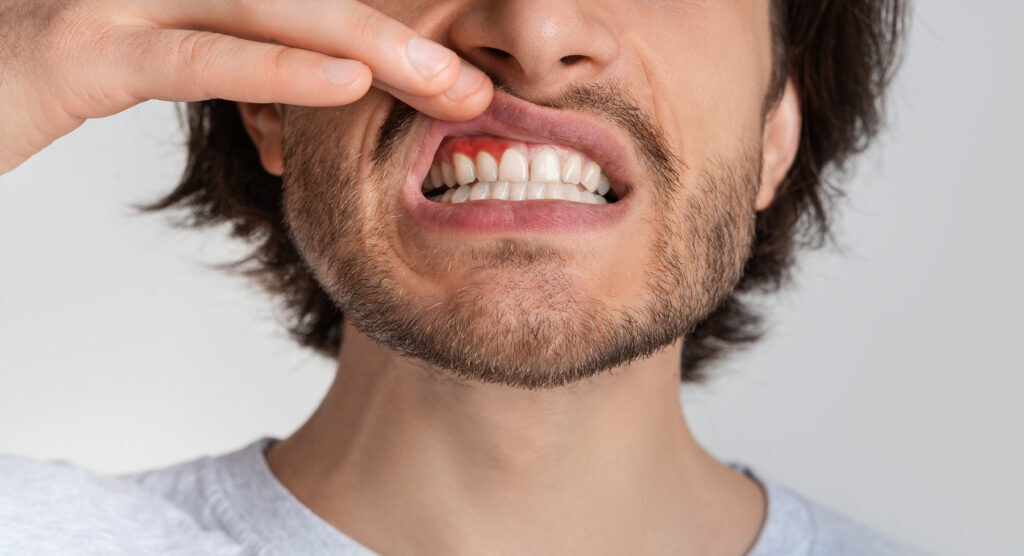
You’re sitting in the dentist’s chair, nodding along to the familiar flossing lecture you’ve been politely ignoring for most of your adult life. Fair enough. It’s hard to get excited about gum health. But it turns out your dentist may have been underselling the pitch.
A study published in January 2026 in Cell Communication and Signaling shows that a common gum disease bacterium can promote breast cancer growth and spread in mice, and the findings hint at a particularly troubling link for people carrying BRCA1 mutations (1). “Floss to help prevent cancer” probably wasn’t on your 2026 bingo card, yet here we are.
Continue reading “From Gum Disease to Breast Cancer: An Oral Bacterium’s Unexpected Journey”