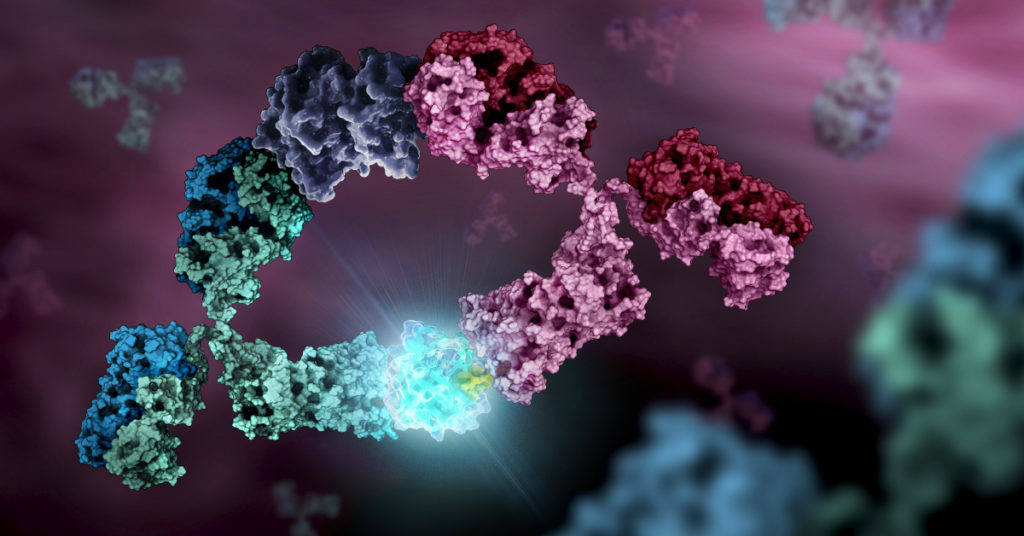
On November 18, 2022, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) announced the approval of the first drug to delay the onset of stage 3 type 1 diabetes (T1D). The monoclonal antibody (mAb) drug, teplizumab, was approved for use in adults and pediatric patients 8 years and older.
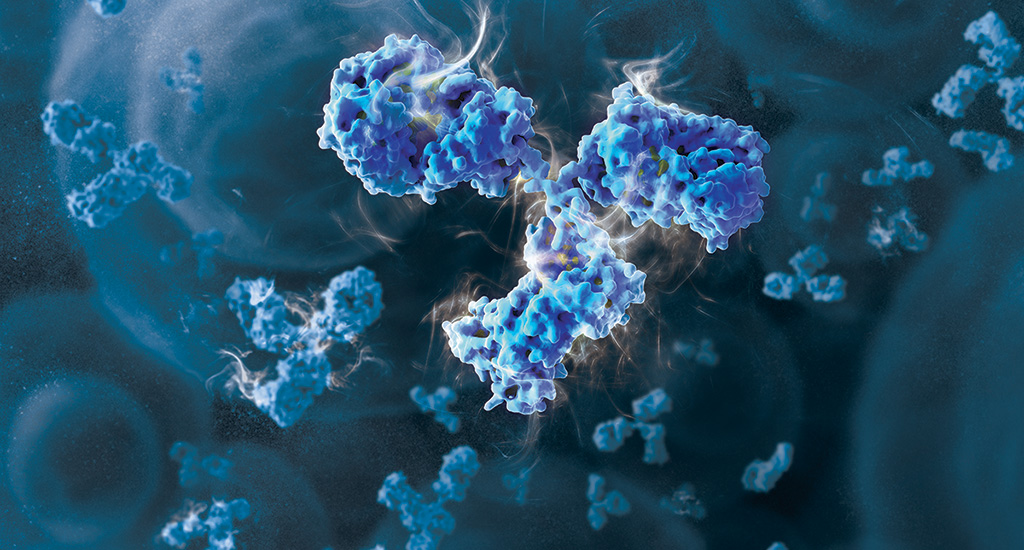
The road to approval has been a bumpy one for the manufacturer, Provention Bio. In 2020, the FDA rejected the application for teplizumab due to several concerns, including the small size of the clinical trial. With the current approval, based on new clinical trial results, Provention Bio confirmed a co-promotion agreement with Sanofi US. The agreement included a $35 million Sanofi equity investment in the company.
Continue reading “Monoclonal Antibody (mAb) Therapy to Delay the Onset of Type 1 Diabetes”