We’ve learned a few important lessons from the COVID-19 pandemic.
Perhaps the most significant one is the importance of an early and rapid global response to the initial outbreak. A coordinated response—including widespread use of masks and other personal protective equipment (PPE), travel restrictions, lockdowns and social distancing—could save lives and reduce long-term health effects (1). Widespread availability of effective vaccines goes hand in hand with these measures.
New Boosters to Fight Omicron
Last month, Pfizer/BioNTech announced the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) had granted emergency use authorization (EUA) for a new adapted-bivalent COVID-19 booster vaccine for individuals 12 years and older. This vaccine combines mRNA encoding the wild-type Spike protein from the original vaccine with another mRNA encoding the Spike protein of the Omicron BA.4/BA.5 subvariants. Moderna also announced FDA EUA for its new Omicron-targeting COVID-19 booster vaccine. The Omicron variant of SARS-CoV-2 shows multiple mutations across its subvariants, and it is currently the dominant SARS-CoV-2 variant of concern across the world.
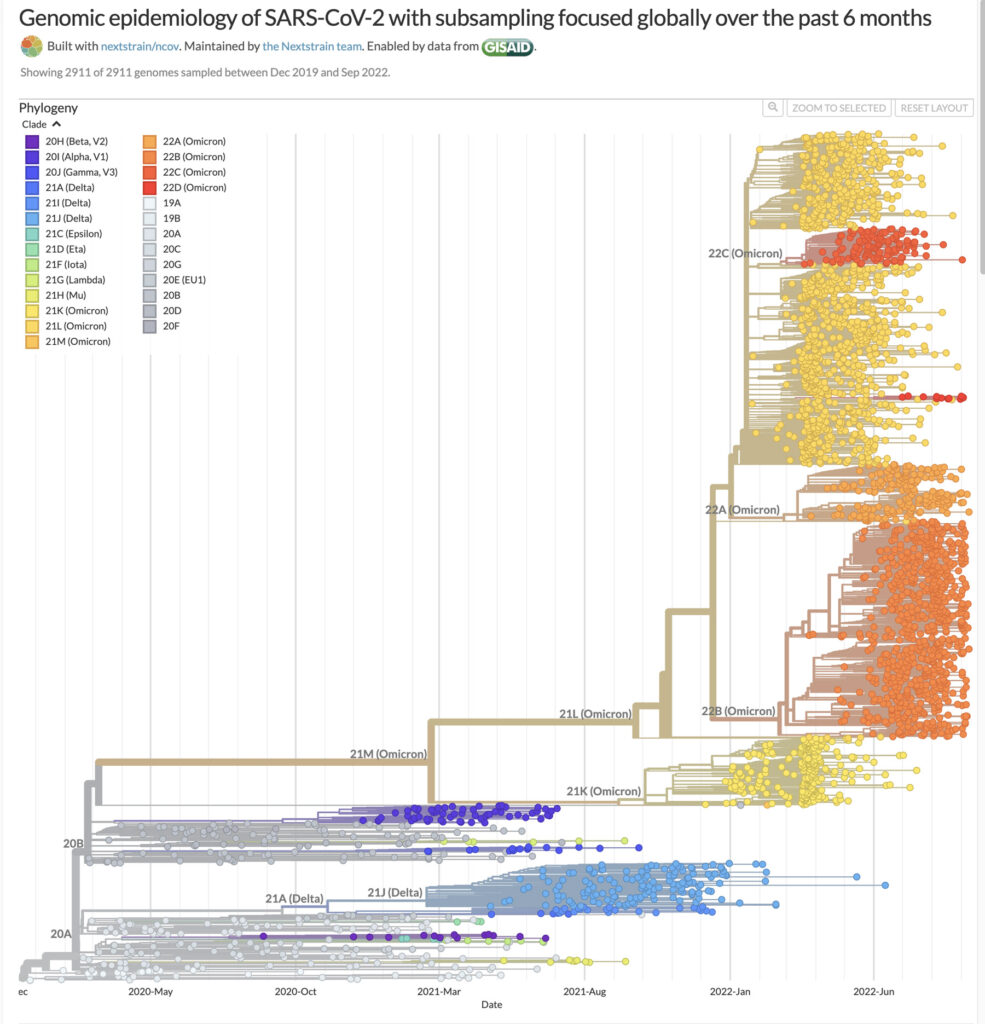
Booster doses of vaccines have become a way of life, both due to declining effectiveness of the original vaccines especially in older adults (2), and the rapid mutation rate of SARS-CoV-2 (3). Clinical data for the new Pfizer/BioNTech booster vaccine showed superior effectiveness in eliciting an immune response against Omicron BA.1 compared to the original vaccine. Previously, Moderna published interim results from an ongoing phase 2-3 clinical trial, showing that the new bivalent booster vaccine elicited a superior neutralizing antibody response against Omicron, compared to its original COVID-19 vaccine (4).
Continue reading “mRNA Vaccine Manufacturing: Responding Effectively to a Global Pandemic”