 As someone who regularly works at a computer both at work and at home, sedentary activity is a part of my daily life. Unfortunately, my desk is the standard kind that requires me to sit on a chair; I can only dream of the kind that has a treadmill to walk and encourage movement as I work. The health consequences of sitting for long periods of time have been covered in research papers and other blogs, but a recent paper highlighted how sitting for extended periods of time can have major health consequences. Continue reading “Stand Up and Walk; Repeat Often”
As someone who regularly works at a computer both at work and at home, sedentary activity is a part of my daily life. Unfortunately, my desk is the standard kind that requires me to sit on a chair; I can only dream of the kind that has a treadmill to walk and encourage movement as I work. The health consequences of sitting for long periods of time have been covered in research papers and other blogs, but a recent paper highlighted how sitting for extended periods of time can have major health consequences. Continue reading “Stand Up and Walk; Repeat Often”
Author: Sara Klink
What Caused the Black Death?

I was confident I knew a few things about the bubonic plague: It was caused by the bacterium Yersinia pestis, which was transmitted to humans by fleas hitching a ride on the back of traveling rats. It spread rapidly and devastated populations around the globe, and because cats, a natural predator of scurrying rodents, had been killed, rats proliferated along with their deadly, infectious cargo. However, until I read a recent PLoS ONE article, I did not realize there was still debate about whether Yersinia pestis was the infectious agent for Black Death, the disease that ravaged 14th century Europe and killed one third of its population.
An Interview with Ed Himelblau, Scientist and Promega Cartoonist
Many visitors to the Promega Web site enjoy the Cartoon Lab, the repository of the creative illustrations of Ed Himelblau updated several times a year. Recently, I had a chance to gain some insight about the man behind the cartoons.
Sara Klink: Could you give some background information about yourself?
Ed Himelblau: I was born in Chicago but grew up in San Diego. I went to UCSD [University of California at San Diego] and majored in biology and minored in art. I liked molecular biology and working in labs so I decided to go to grad school. I went to the University of Wisconsin at Madison to get a Ph.D. in the Cell and Molecular Biology program. My first academic job was teaching biology at Southampton College in New York. After several years on Long Island, I moved to my current job teaching and doing research in the Biological Sciences Department at Cal Poly [California Polytechnic State University] in San Luis Obispo, CA.
S.K.: Why did you decide to become a scientist?
E.H.: Playing in tidepools as a kid had something to do with it. As an undergraduate I thought working in a lab sounded cool. When I started working in a lab, I thought the work was interesting and the people were a lot of fun to be around. Then I started to appreciate what it really meant to do experiments and learn about how plants grow and develop.
Finding the Next Generation of Antibiotics: Closthioamide
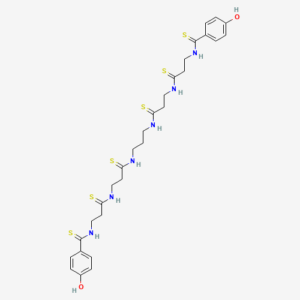
Mention the word penicillin and it conjures up images of mold growing on bacterial culture plates and Dr. Alexander Fleming observing that the mold had killed the surrounding bacteria, ushering in the age of antibiotics. Bacterial infections could easily be treated with penicillin or any one of the bewildering array of new antibiotics continually being discovered. The result of using these antimicrobial drugs: numerous lives were saved and human health improved. However, bacteria are clever organisms and as quickly as humans developed an antibiotic to treat infection, the microbes would find a way around the bacteriostatic or bacteriocidal compound. It is a scary world where antibiotics are rendered impotent and fewer and fewer weapons are left in the arsenal to treat multidrug-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and hospital-acquired drug-resistant Gram-negative bacteria (e.g., Acinetobacter baumannii).
Continue reading “Finding the Next Generation of Antibiotics: Closthioamide”A Sensitive, Universal Kinase Assay Ideal for Use with Low-Turnover Enzymes
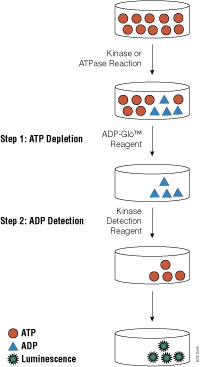
Promega carries a large array of luminescent-based assays to measure cellular events such as viability, cytochrome P450 activity and apoptosis. Recently, we launched a new universal, homogeneous, high-throughput screening method called the ADP-Glo™ Kinase Assay, which measures kinase activity by quantifying the amount of ADP produced during a kinase reaction. While we already offer the Kinase-Glo™ Assays for assessing the quantity of ATP remaining after a kinase reaction, these assays are not ideal for use with low-activity kinases.
Continue reading “A Sensitive, Universal Kinase Assay Ideal for Use with Low-Turnover Enzymes”
